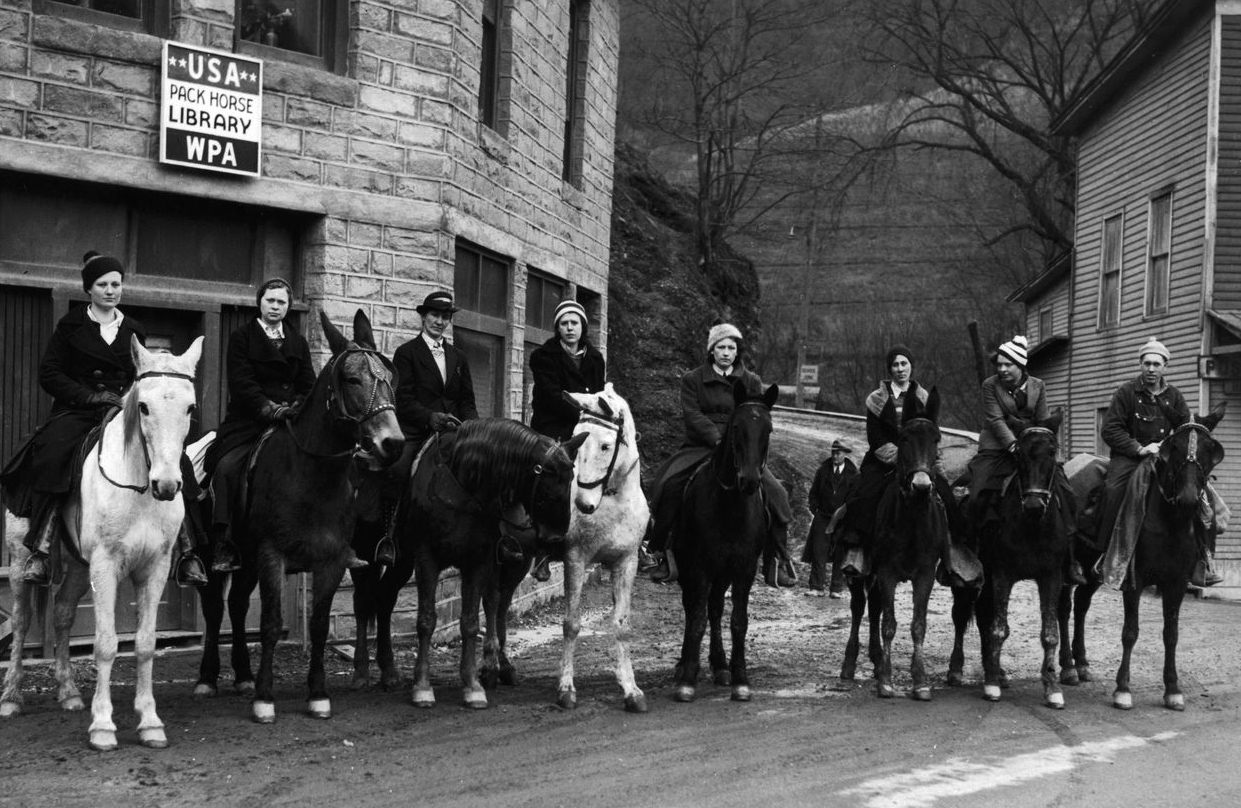
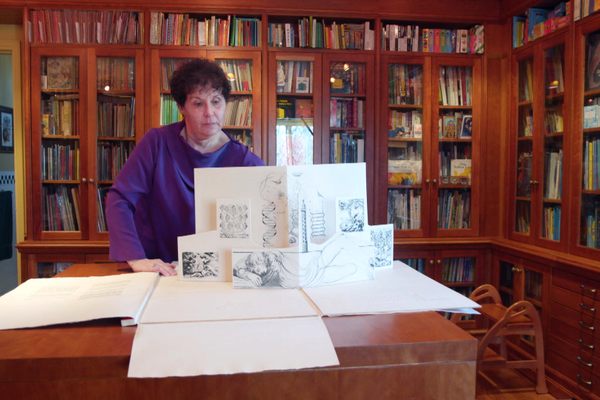
The Women Who Rode Miles on Horseback to Deliver Library Books
Librarians are amazing.
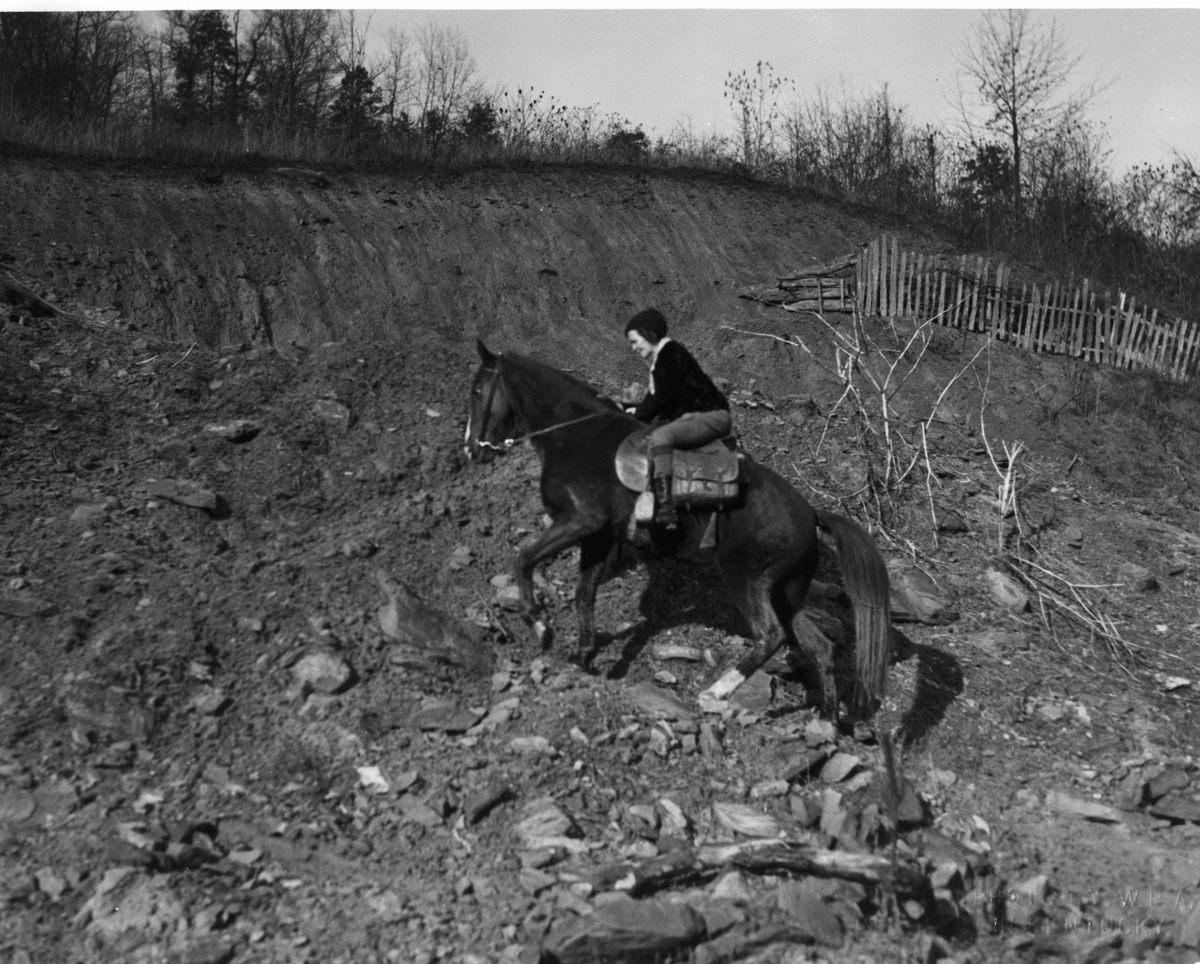
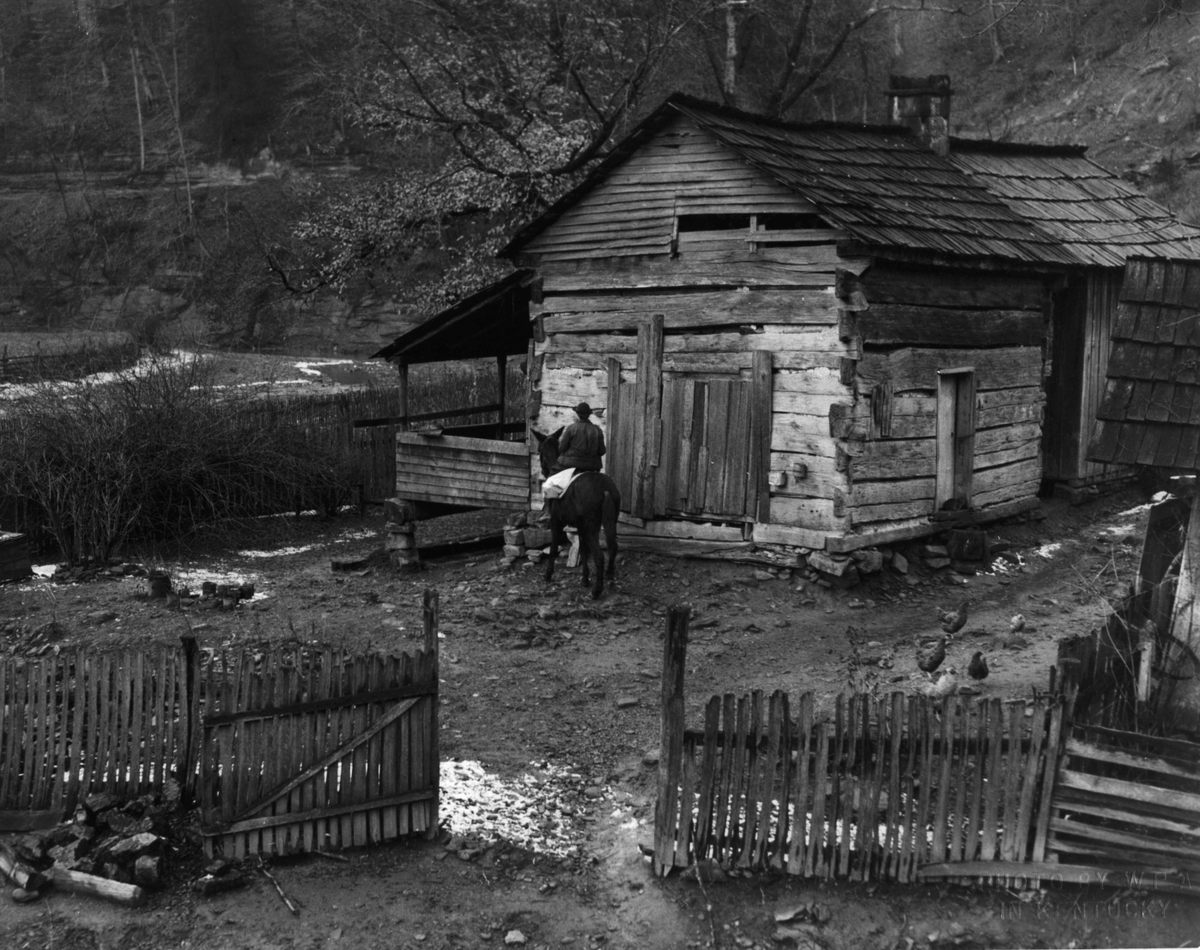
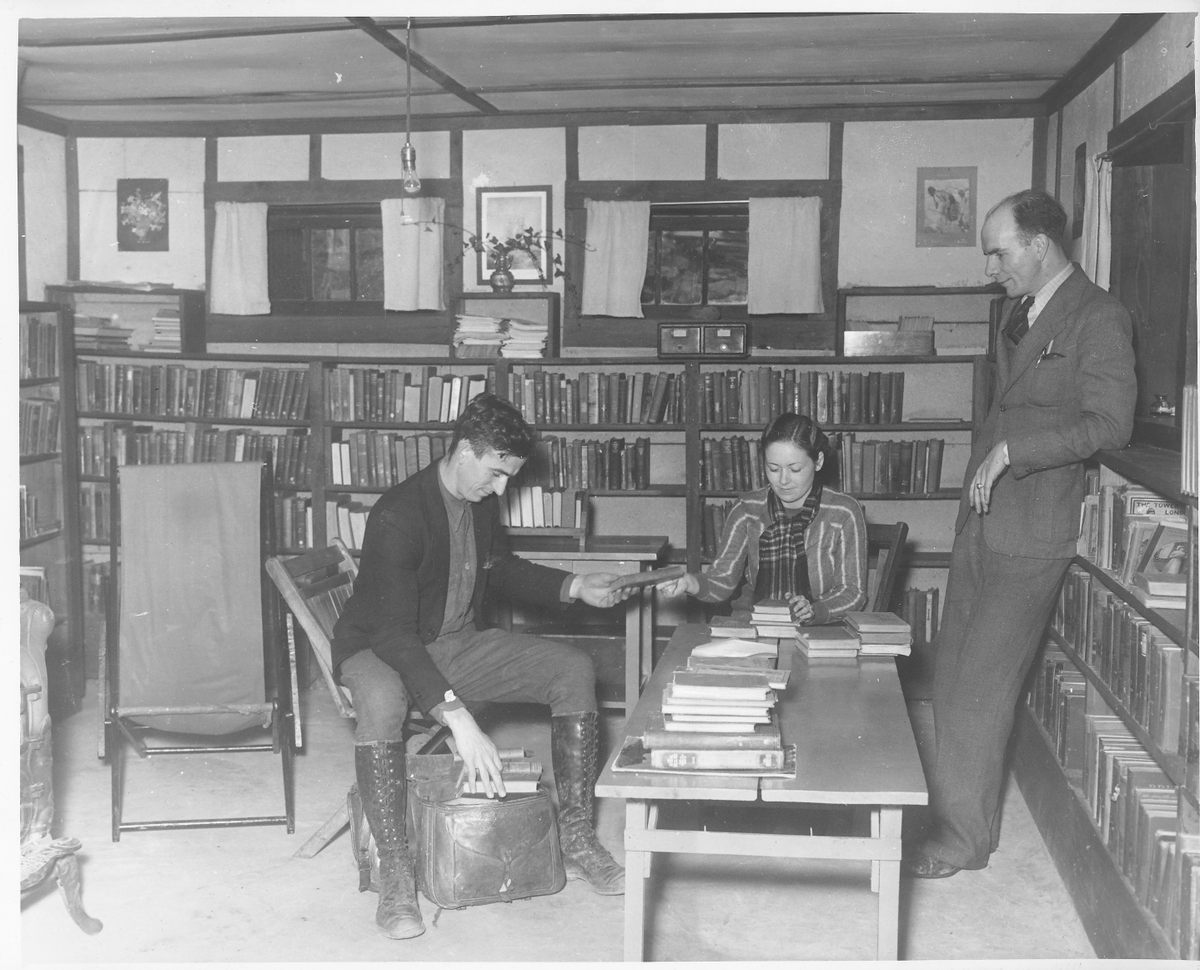
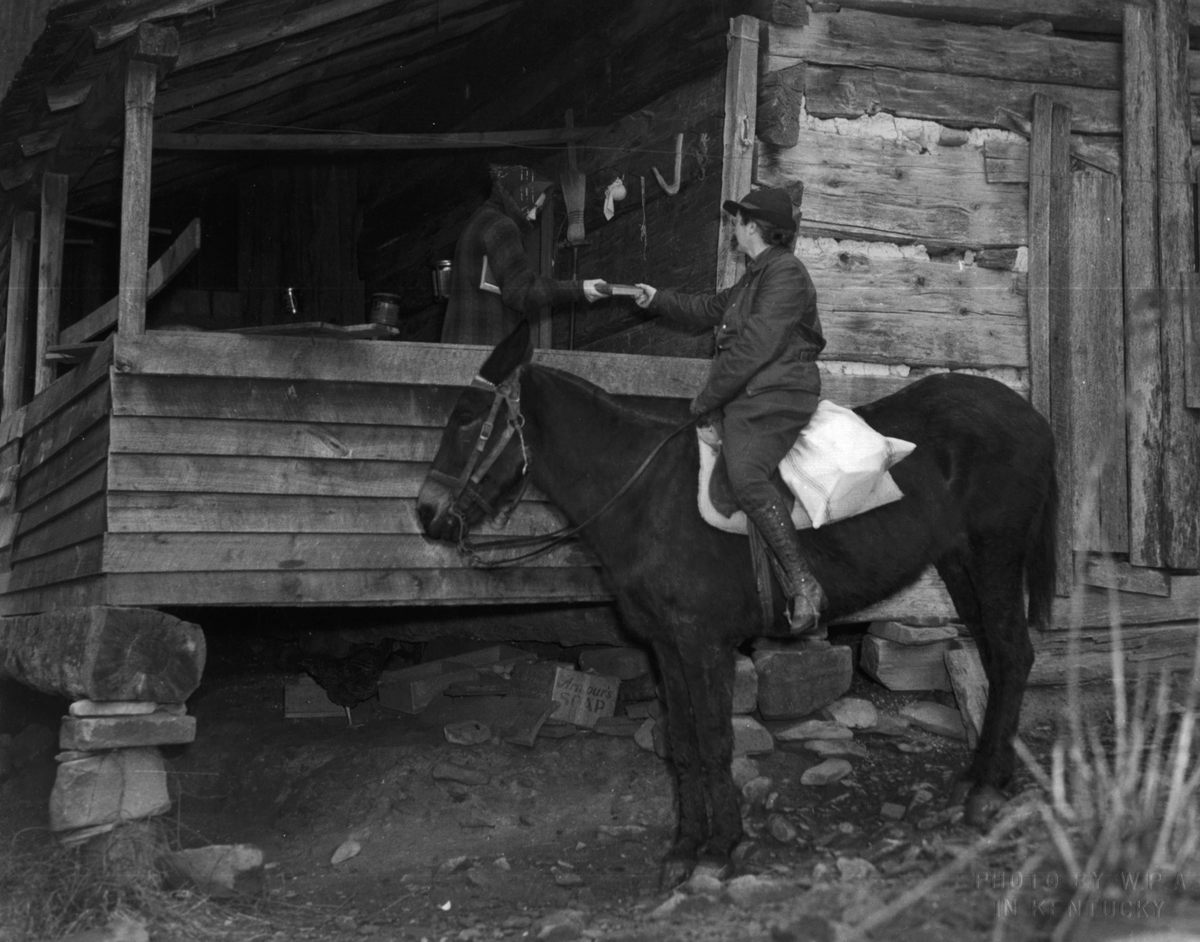
They were known as the “book women.” They would saddle up, usually at dawn, to pick their way along snowy hillsides and through muddy creeks with a simple goal: to deliver reading material to Kentucky’s isolated mountain communities.
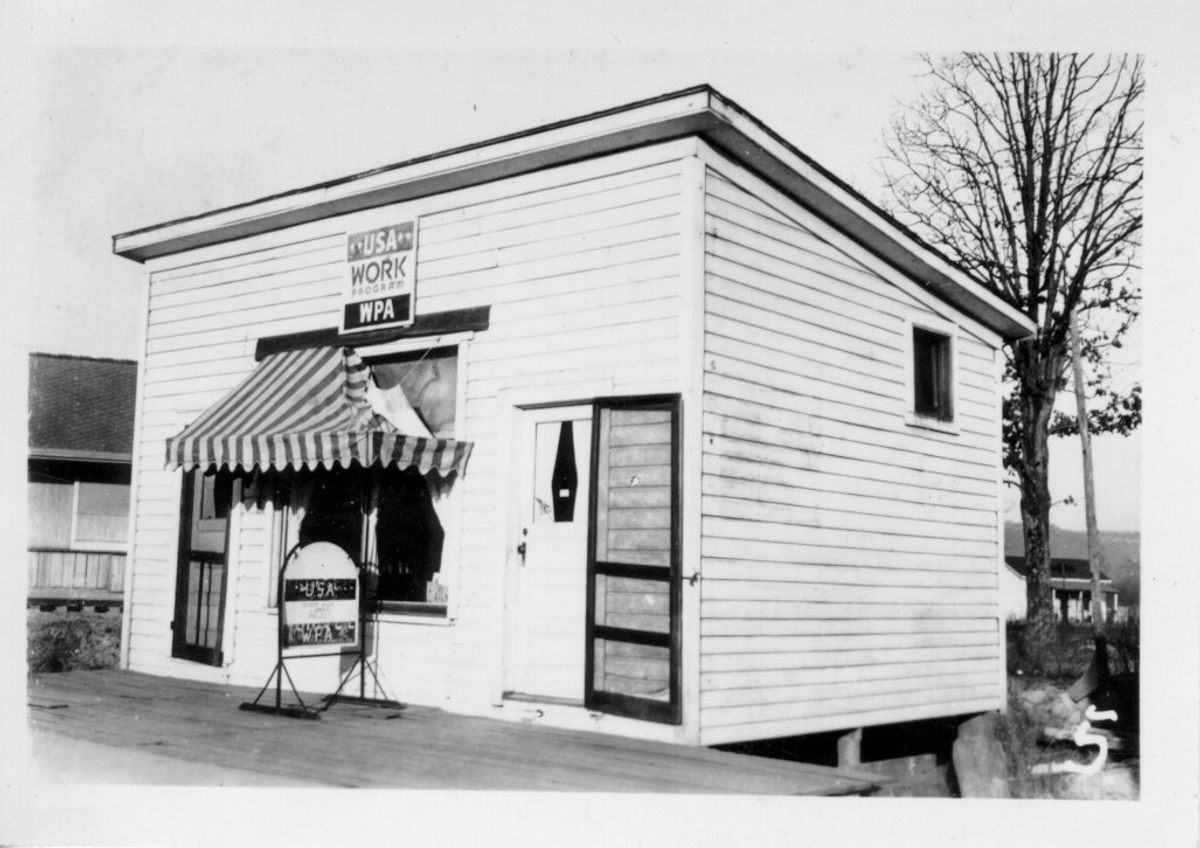
The Pack Horse Library initiative was part of President Franklin Roosevelt’s Works Progress Administration (WPA), created to help lift America out of the Great Depression, during which, by 1933, unemployment had risen to 40 percent in Appalachia. Roving horseback libraries weren’t entirely new to Kentucky, but this initiative was an opportunity to boost both employment and literacy at the same time.
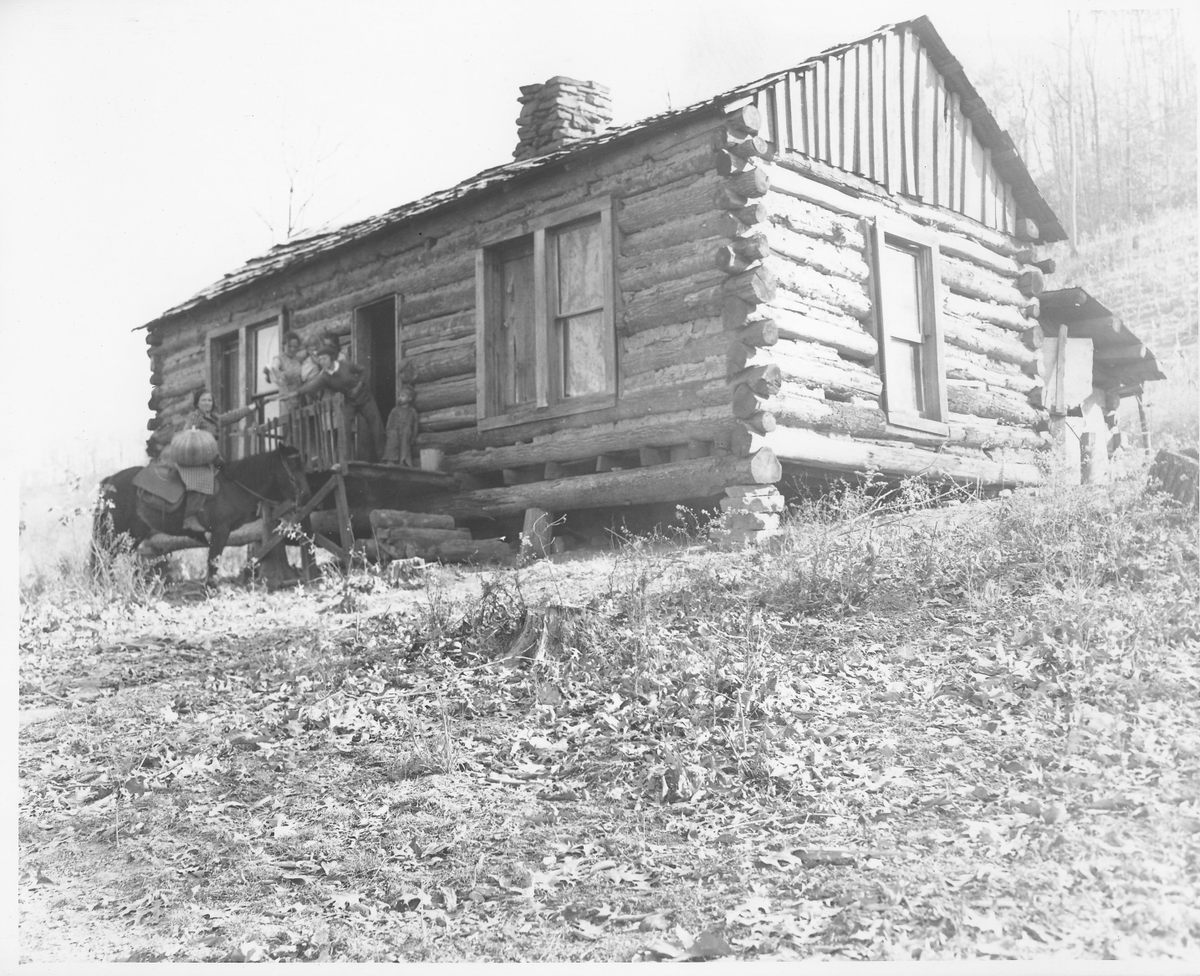

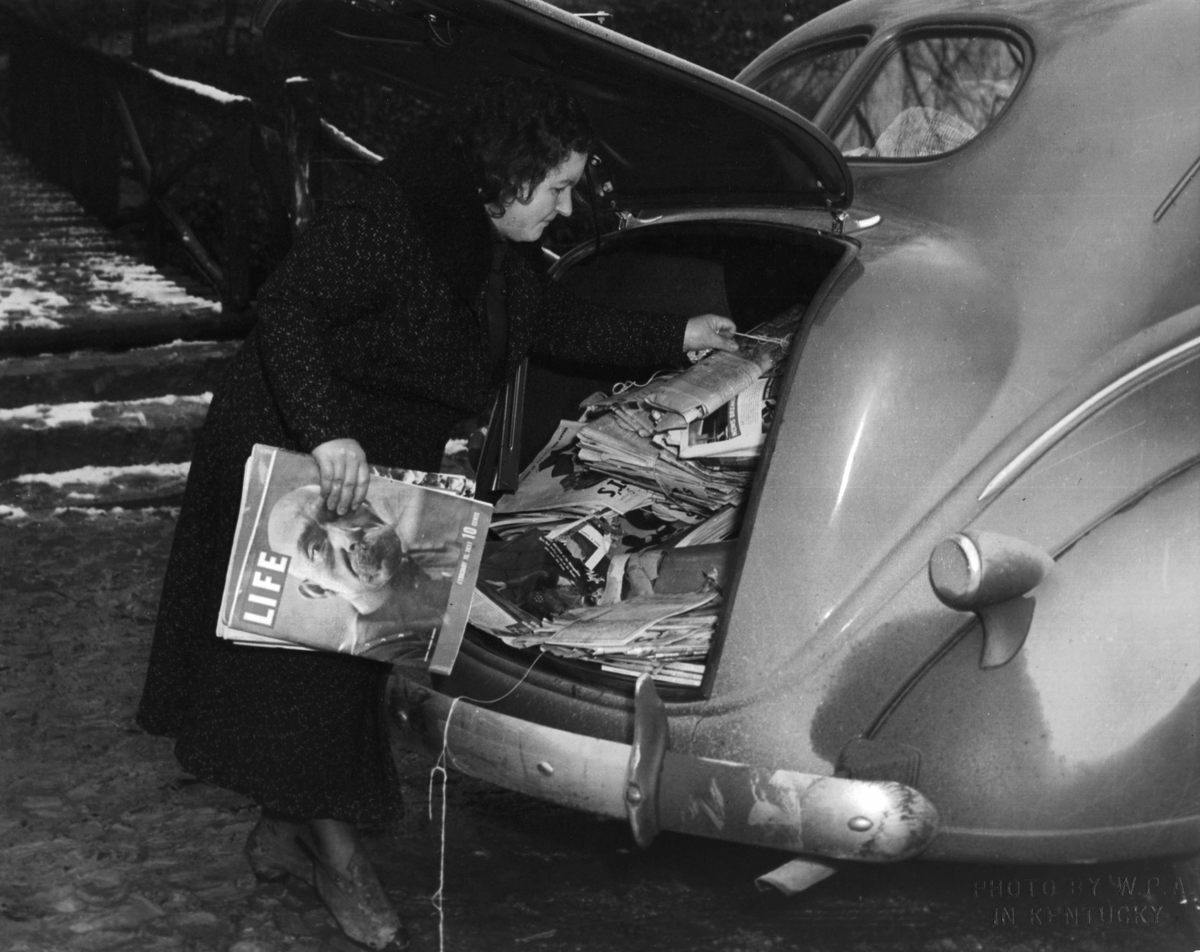
The WPA paid the salaries of the book carriers—almost all the employees were women, making the initiative unusual among WPA programs—but very little else. Counties had to have their own base libraries from which the mounted librarians would travel. Local schools helped cover those costs, and the reading materials—books, magazines, and newspapers—were all donated. In December 1940, a notice in the Mountain Eagle newspaper noted that the Letcher County library “needs donations of books and magazines regardless of how old or worn they may be.”
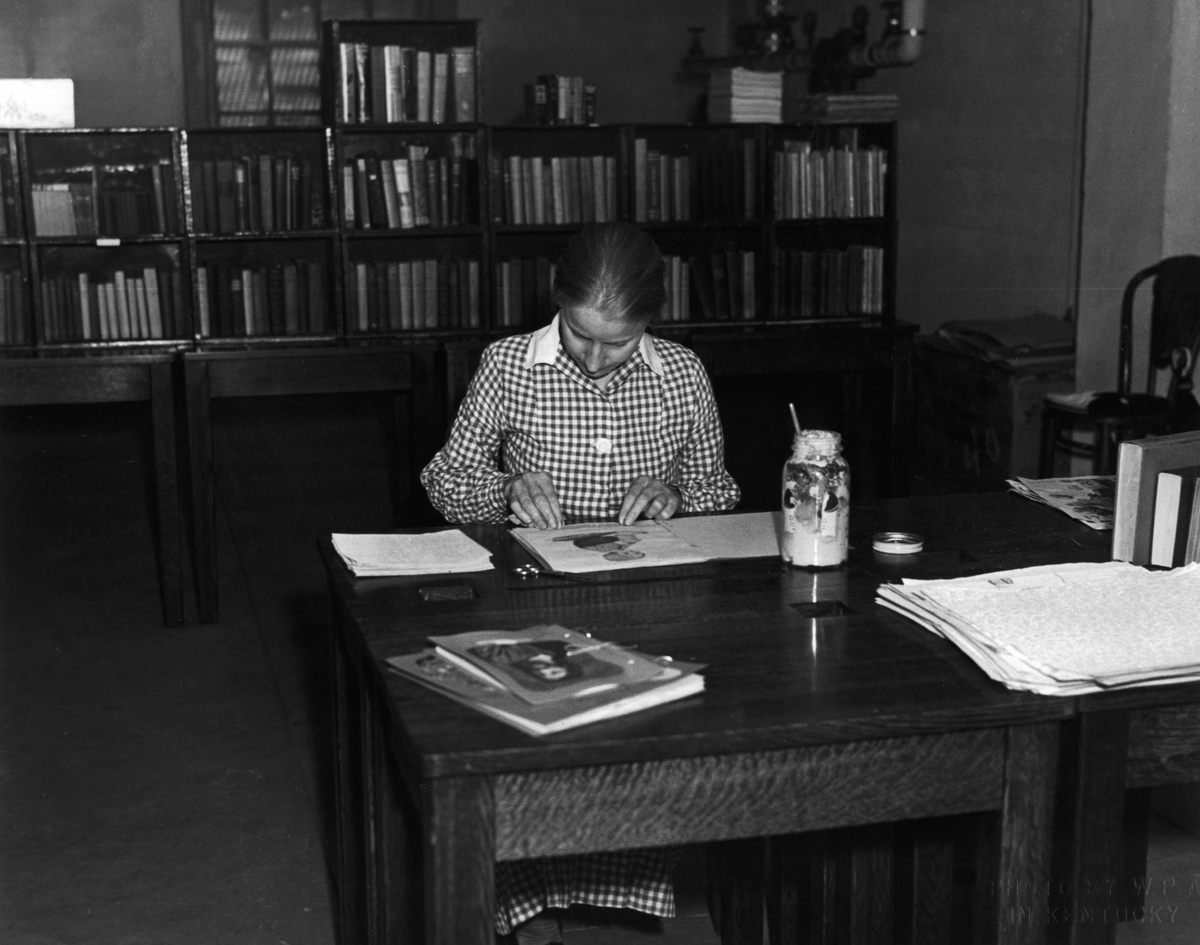
Old magazines and newspapers were cut and pasted into scrapbooks with particular themes—recipes, for example, or crafts. One such scrapbook, which still is held today at the FDR Presidential Library & Museum in Hyde Park, New York, contains recipes pasted into a notebook with the following introduction: “Cook books are popular. Anything to do with canning or preserving is welcomed.” Books were repaired in the libraries and, as historian Donald C. Boyd notes, old Christmas cards were circulated to use as bookmarks and prevent damage from dog-eared pages.
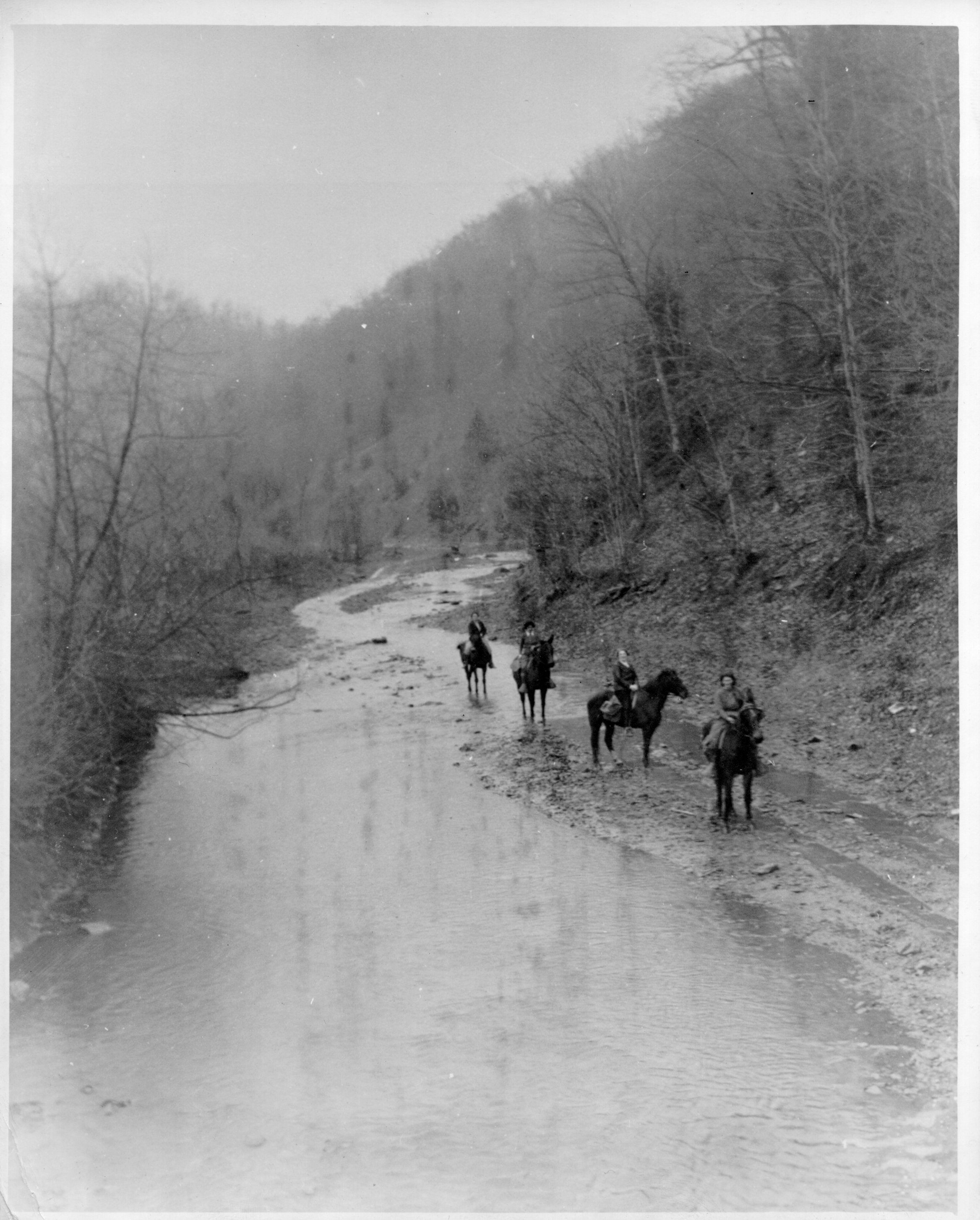

The book women rode 100 to 120 miles a week, on their own horses or mules, along designated routes, regardless of the weather. If the destination was too remote even for horses, they dismounted and went on foot. In most cases, they were recruited locally—according to Boyd, “a familiar face to otherwise distrustful mountain folk.”
By the end of 1938, there were 274 librarians riding out across 29 counties. In total, the program employed nearly 1,000 riding librarians. Funding ended in 1943, the same year the WPA was dissolved as unemployment plummeted during wartime. It wasn’t until the following decade that mobile book services in the area resumed, in the form of the bookmobile, which had been steadily increasing in popularity across the country.
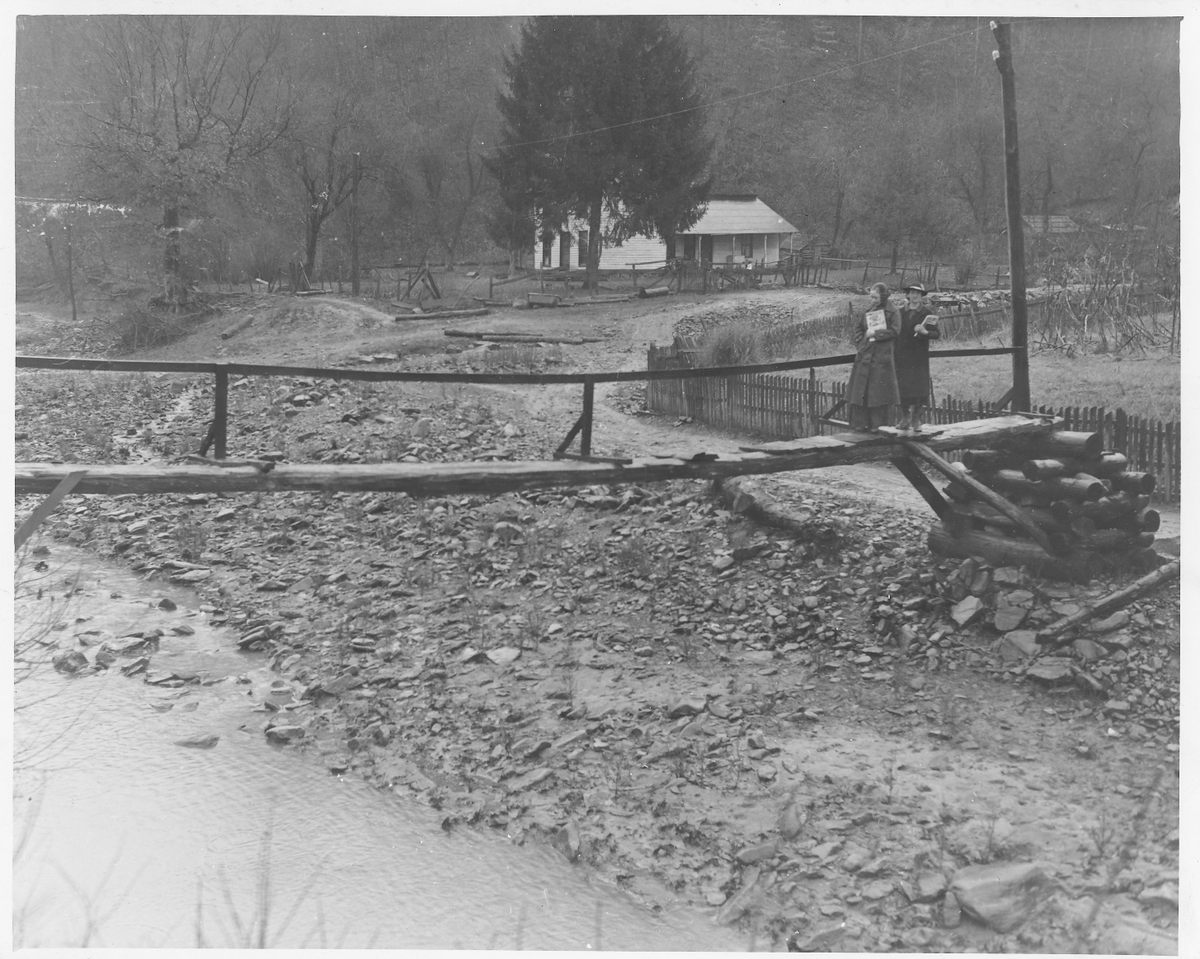

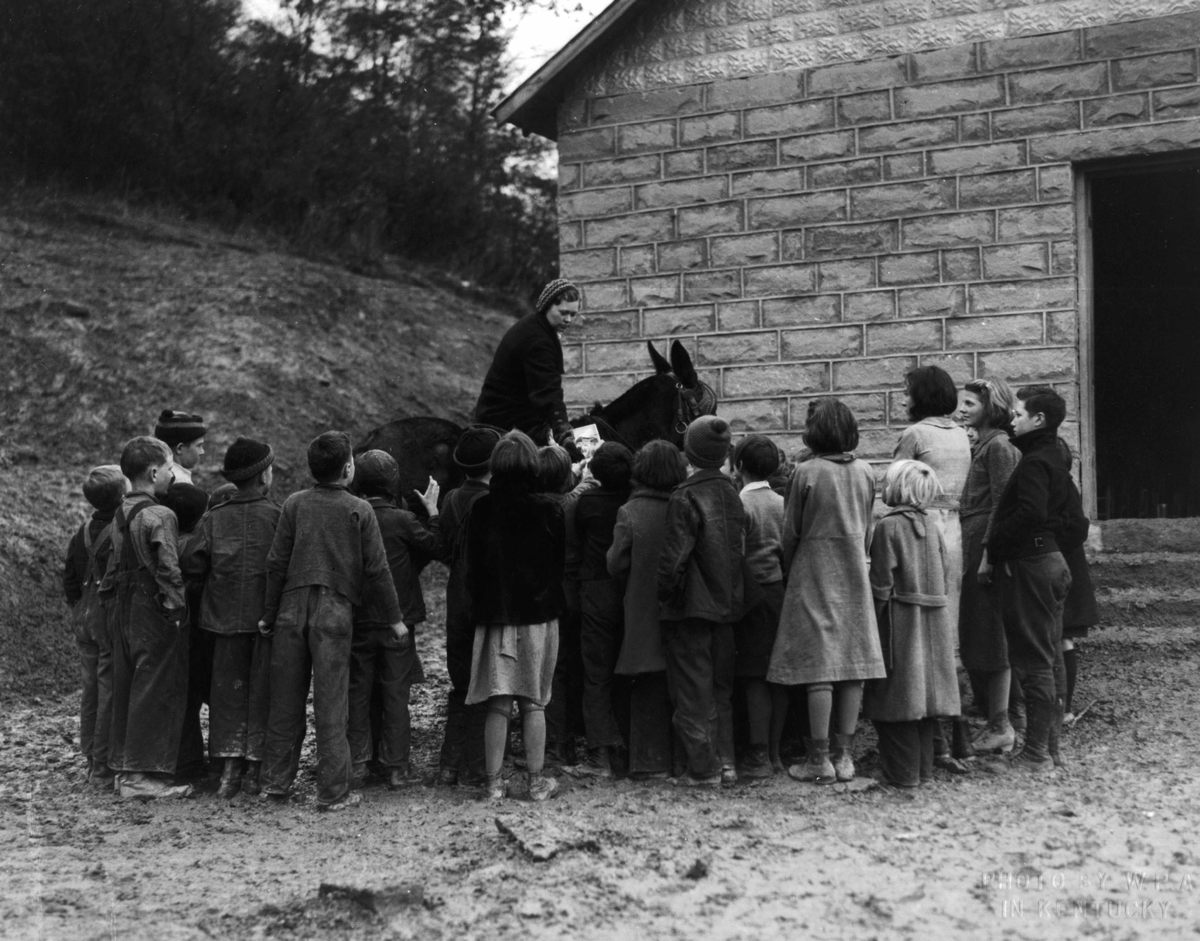
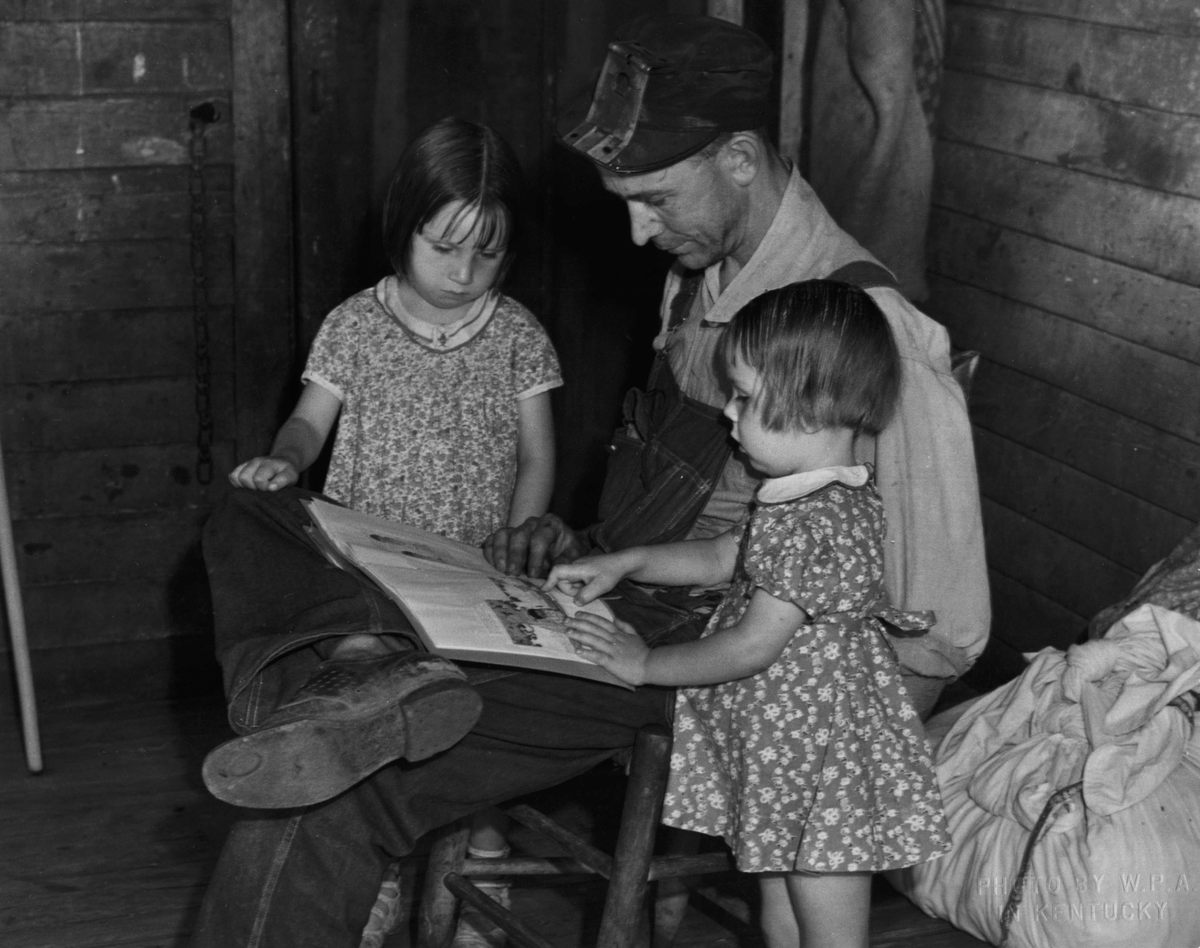
In addition to providing reading materials, the book women served as touchstones for these communities. They tried to fill book requests, sometimes stopped to read to those who couldn’t, and helped nurture local pride. As one recipient said, “Them books you brought us has saved our lives.” In the same year as the call for books, the Mountain Eagle exalted the Letcher County library: “The library belong to our community and to our county, and is here to serve us … It is our duty to visit the library and to help in every way that we can, that we may keep it as an active factor in our community.”
Atlas Obscura has a selection of images of the Kentucky pack horse librarians.
























Follow us on Twitter to get the latest on the world's hidden wonders.
Like us on Facebook to get the latest on the world's hidden wonders.
Follow us on Twitter Like us on Facebook